She will not be having a Valentine’s Date this Year. Meet the All Female Species: Marbled Crayfish.
Marbled crayfish (Marmorkrebs) is a species that has gained a great deal of publicity and interest from the scientific community, because of its parthenogenetic reproduction, its invasive nature and because of the fact that its behavior can be used as a very interesting research model.1
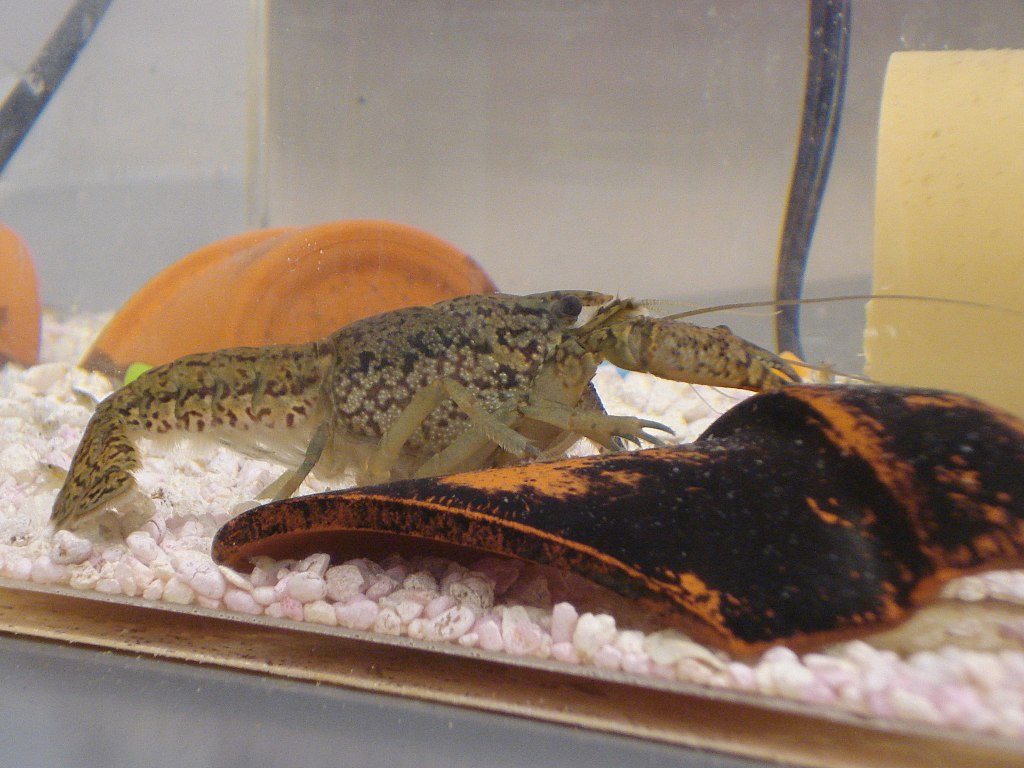

Marbled crayfish was discovered in German aquarium trade in 1995 and since then it became a popular pet. It is the only species known for its parthenogenesis2 among the approximately 15000 crustaceans.
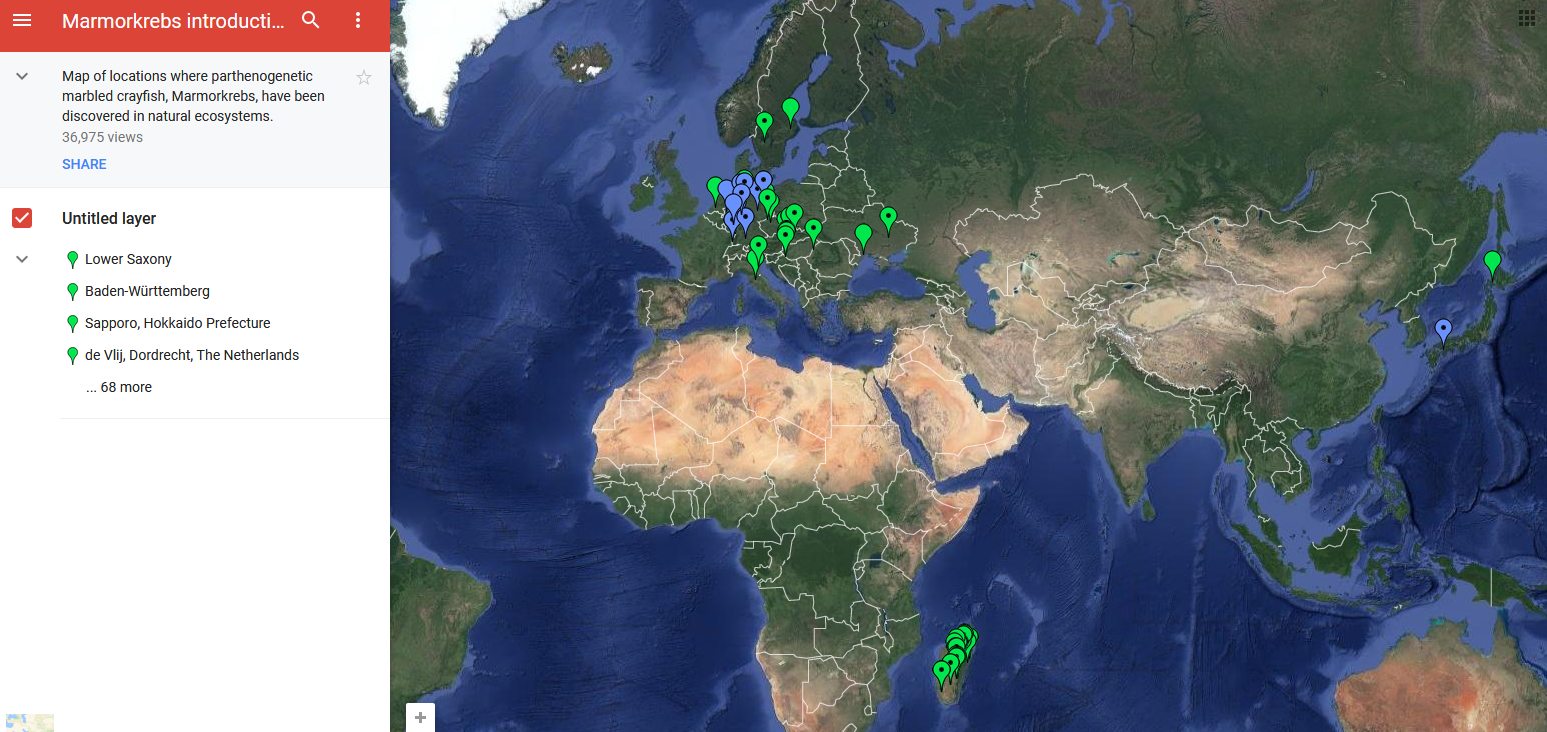
A recent paper 3 revealed that the marbled crayfish (Procambarus virginalis) represent a rather invasive species, having populated many diverse fresh water habitats. The analysis confirmed that they are related to the ‘slough crayfish’ and that they have a triploid genotype4.
Apparently this crayfish has originated through a macro mutation in P. fallax. As this species first appeared in the German aquarium trade, it was quickly distributed and this resulted in its spreading throughout Europe and Madagascar.
The potential ecological threat should not be overseen, as it appears this species could out compete native forms even if only a single specimen would be released into European lakes or rivers
Dr Wolfgang Stein4 states that in only a few years the marbled crayfish managed to grow from occupying a space the size of Rhode Island to occupying a space the size of Ohio
Additionally, the paper’s results show that they have three sets of chromosomes:
Our results show that the marbled crayfish genome consists of two almost identical copies of one genotype and a third copy of a comparably divergent, but still homologous genotype. These findings are consistent with the model that the marbled crayfish genome originated from an autopolyploid P. fallax gamete and the mating of two distantly related P. fallax individuals possibly from distant populations and in captivity.
What is very important to mention is that the recent research could set the ground for additional research regarding understanding the early stages of tumors.
"What we see in slow motion with the marbled crayfish evolution is something that happens during the very early stages of tumor formation," Frank Lyko5 says.
This one of a kind species was first discovered by German hobbyists in 1995 and ever since it has been an interesting speciment for research due to its unique characteristics.
All the Marmokrebs [German translation as marbled crab] are females and can reproduce without sex. This alone qualifies as a model organism for research. They are also very invasive, as they have been able to establish population in many countries, being a damage in the ecosystem and they have a vast scientific interest as their behavior may help in understanding the early stages of tumor creations.
It should be highlighted that Marbled Crayfish should not be kept in outdoor tanks or be given any possibility to be released into natural ecosystems. 6
source
In North America, Marmorkrebs are prohibited in Missouri (since 2011) and Tennessee (since 2015). The European Union banned possession, trade, transport, production, and release of Marmorkrebs (and several other crayfish species) in 2016.
Please find below sources for further reading
Source – bio.biologists.org
Source – Nature; Ecology & Evolution
Source – National Geographic
Source – faculty.utrgv.edu
Google Map with locations where parthenogenetic marbled crayfish have been discovered in natural ecosystems
nature.com
cabi.org
nature.com








Comments